Carotid duplex
Scan - carotid duplex; Carotid ultrasound; Carotid artery ultrasound; Ultrasound - carotid; Vascular ultrasound - carotid; Ultrasound - vascular - carotid; Stroke - carotid duplex; TIA - carotid duplex; Transient ischemic attack - carotid duplexCarotid duplex is an ultrasound test that shows how well blood is flowing through the carotid arteries. The carotid arteries are located in the neck. They supply blood directly to the brain.
The Basics
Tests for carotid artery ultrasound
Carotid duplex
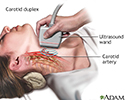
Carotid duplex is an ultrasound procedure performed to assess blood flow through the carotid artery to the brain. High-frequency sound waves are directed from a hand-held transducer probe to the area. These waves bounce off the arterial structures and produce a 2-dimensional image on a monitor, which will make obstructions or narrowing of the arteries visible.
Carotid duplex
illustration
Carotid duplex ultrasound
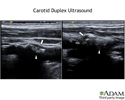
This duplex Doppler sonogram shows an irregular plaque in the carotid artery. This type of plaque can cause clots to form, which can cause a stroke. Doppler studies are used to help identify these types of plaques ahead of time to prevent a stroke from happening.
Carotid duplex ultrasound
illustration
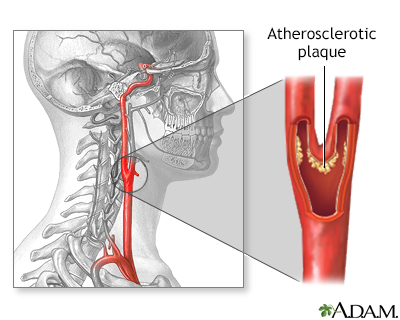
Atherosclerosis of internal carotid artery
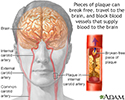
The build-up of plaque in the internal carotid artery may lead to narrowing and irregularity of the artery's lumen, preventing proper blood flow to the brain. More commonly, as the narrowing worsens, pieces of plaque in the internal carotid artery can break free, travel to the brain and block blood vessels that supply blood to the brain. This leads to stroke, with possible paralysis or other deficits.
Atherosclerosis of internal carotid artery
illustration
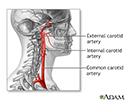
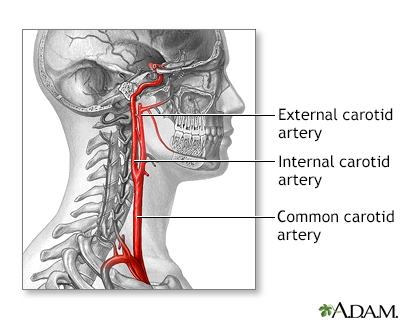
Carotid artery anatomy
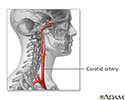
There are four carotid arteries, two on each side of the neck: right and left internal carotid arteries, and right and left external carotid arteries. The carotid arteries deliver oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the head and brain.
Carotid artery anatomy
illustration
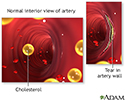
Arterial tear in internal carotid artery
Cholesterol may build-up in the lining of an internal carotid artery.
Arterial tear in internal carotid artery
illustration
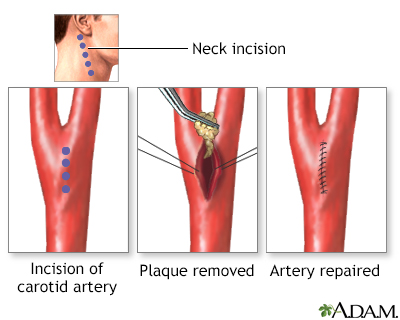
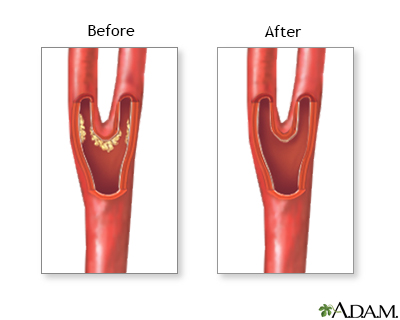
Carotid artery surgery - series
Presentation
Carotid duplex
Carotid duplex is an ultrasound procedure performed to assess blood flow through the carotid artery to the brain. High-frequency sound waves are directed from a hand-held transducer probe to the area. These waves bounce off the arterial structures and produce a 2-dimensional image on a monitor, which will make obstructions or narrowing of the arteries visible.
Carotid duplex
illustration
Carotid duplex ultrasound
This duplex Doppler sonogram shows an irregular plaque in the carotid artery. This type of plaque can cause clots to form, which can cause a stroke. Doppler studies are used to help identify these types of plaques ahead of time to prevent a stroke from happening.
Carotid duplex ultrasound
illustration
Atherosclerosis of internal carotid artery
The build-up of plaque in the internal carotid artery may lead to narrowing and irregularity of the artery's lumen, preventing proper blood flow to the brain. More commonly, as the narrowing worsens, pieces of plaque in the internal carotid artery can break free, travel to the brain and block blood vessels that supply blood to the brain. This leads to stroke, with possible paralysis or other deficits.
Atherosclerosis of internal carotid artery
illustration
Carotid artery anatomy
There are four carotid arteries, two on each side of the neck: right and left internal carotid arteries, and right and left external carotid arteries. The carotid arteries deliver oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the head and brain.
Carotid artery anatomy
illustration
Arterial tear in internal carotid artery
Cholesterol may build-up in the lining of an internal carotid artery.
Arterial tear in internal carotid artery
illustration
Carotid artery surgery - series
Presentation
Carotid duplex
Scan - carotid duplex; Carotid ultrasound; Carotid artery ultrasound; Ultrasound - carotid; Vascular ultrasound - carotid; Ultrasound - vascular - carotid; Stroke - carotid duplex; TIA - carotid duplex; Transient ischemic attack - carotid duplexCarotid duplex is an ultrasound test that shows how well blood is flowing through the carotid arteries. The carotid arteries are located in the neck. They supply blood directly to the brain.
The Basics
Tests for carotid artery ultrasound
Carotid duplex
Scan - carotid duplex; Carotid ultrasound; Carotid artery ultrasound; Ultrasound - carotid; Vascular ultrasound - carotid; Ultrasound - vascular - carotid; Stroke - carotid duplex; TIA - carotid duplex; Transient ischemic attack - carotid duplexCarotid duplex is an ultrasound test that shows how well blood is flowing through the carotid arteries. The carotid arteries are located in the neck. They supply blood directly to the brain.
The Basics
Tests for carotid artery ultrasound
Review Date: 7/26/2022
Reviewed By: Evelyn O. Berman, MD, Assistant Professor of Neurology and Pediatrics at University of Rochester, Rochester, NY. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.